Working with Coverage Tables and Coordination of Benefits
This document provides instructions for creating coverage table templates and adding exceptions in coverage, updating insurance plans, editing coverage tables and exceptions in coverage for insurance plans in Dentrix Ascend. This document also provides an explanation of how Dentrix Ascend calculates insurance estimates.
1. Coverage table templates
Creating coverage table templates
Creating coverage table templates
Dentrix Ascend provides two default templates (which are named "All Procedures") and allows you to create various templates that you can use in your organization for setting up the coverage tables of insurance plans.
Note: Coverage table templates are global (available to all locations across your organization).
To create a coverage table template
-
On the Settings menu, under Production, click (or tap) Coverage Tables.
The Coverage Table Setup page opens.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Create new - To make an all new coverage table template, click (or tap) New Coverage Table.

-
Base on existing - To make a coverage table template based on an existing template, select the template that is similar to the one that you want to create.

Note: The templates are grouped by type. Expand Insurance Coverage, % to view templates that are based on insurance coverage percentages, or expand Patient Copayment, $ to view templates that are based on fixed, patient copayments.
The options for adding or editing the coverage table template appear. The options that are available depend on whether you are creating a new template or making one that is based on an existing template and whether the template is based on insurance coverage percentages or fixed, patient copayments.
New

Based on Existing

Insurance Coverage, %

Patient Copayment, $
-
-
Enter or change the Template name. The name must be unique relative to the templates of the same type (Insurance Coverage, % or Patient Copayment, $).
-
If you are creating a new template, from the Type list, select either Insurance Coverage, % or Patient Copayment, $ to specify whether the coverage should be based on a percentage or a fixed amount, respectively. Once you save the template, you cannot change the type.
With a Type selected, the options for creating the template become available.

Insurance Coverage, %

Patient Copayment, $
-
Do one of the following:
-
For an Insurance Coverage, % template, add, edit, and delete the procedure code ranges as needed.
Do the following:
-
Click (or tap) Add Range to add a procedure code range, or select an existing range to edit that range.

-
Set up the following options for that range as needed:
-
Code Range - The ADA or custom procedure code range. These boxes accept dashes (-), periods (.), numbers, and letters, and they can be up to 10 characters in length. Make sure there are not any overlaps and gaps in the sequence between the starting and ending codes in the range and between other ranges.
You can include an alias procedure codes in a range by typing a period (.) in either box. The Code Range boxes change to allow for entering suffixes. Enter a suffix in either or both suffix boxes. If you need a period in either of the main code boxes (the boxes to the left of the suffix boxes), you must type the period again in that box.

Note: When you change a range and then click (or tap) somewhere else, the text of the range that you modified turns bold. Also, any ranges that overlap or that are invalid become highlighted in red, and you cannot save the changes to the coverage table until those errors are resolved.
-
Category - The procedure category for the procedures in the range.
-
Deductible Type - The type of deductible that the procedures in the range apply to.
-
Coverage % - The percent that the insurance carrier pays on covered charges (after any deductible, up to any allowed amount, and up to any maximum allowed benefit) for procedures in the range.
-
-
Repeat the steps a - b for any other ranges that you want to add or edit.
-
To delete a range, click (or tap) the corresponding Remove button
 , and then click (or tap) Delete on the confirmation message that appears.
, and then click (or tap) Delete on the confirmation message that appears.Important: If you are deleting the only range in the coverage table, the entire template will be deleted. However, you cannot delete all the ranges in the default template (which is named "All Procedures").
-
-
For a Patient Copayment, $ template, add, edit, and delete the procedure codes as needed.
Do the following:
-
To add procedures codes, do the following:
-
Click (or tap) Add Procedure.

The Add Procedures dialog box appears.

-
Select the checkboxes of the procedure codes that you want to add to the coverage table. You can select or deselect the checkbox in the column header to select and deselect all the procedure codes at the same time.
-
Click (or tap) Add Checked.
Note: If you are adding procedure codes to a coverage table that already has procedure codes, the procedure codes are added at the top of the table, which might not be the correct order; however, when you save the template, the procedure codes will be listed in the correct order.
-
-
To edit an existing or newly-added procedure code, select it.

-
Set up the following options for that code as needed:
-
Deductible Type - The type of deductible that the procedure applies to.
-
Copayment $ - The patient co-pay. Patients will pay the specified amount for the procedure.
-
-
Repeat the steps a - c for any other codes that you want to add or edit.
-
To delete a code, click (or tap) the corresponding Remove button
 , and then click (or tap) Delete on the confirmation message that appears.
, and then click (or tap) Delete on the confirmation message that appears.Important: If you are deleting the only code in the coverage table, the entire template will be deleted. However, you cannot delete all the codes in the default template (which is named "All Procedures").
-
-
-
To add, edit, or delete exceptions to the coverage for specific procedures, click (or tap) Manage Exceptions.
-
Do one of the following:
-
For an all new template, click (or tap) Create.
-
For a template based on another, click (or tap) Save As New Template.
-
Adding exceptions in coverage table templates
Adding exceptions in coverage table templates
You can add exceptions to the percentage covered by insurance for a procedure or range of procedures in any of the coverage table templates.
Important:
-
The exceptions in coverage tables of the type "Insurance Coverage, %" are used by Dentrix Ascend to automatically calculate insurance estimates.
-
The exceptions in coverage tables of the type "Patient Copayment, $" are not used by Dentrix Ascend to automatically calculate insurance estimates.
Notes:
-
If a patient has dual coverage, the exceptions of the primary insurance coverage are used.
-
A posted procedure with an exception will have a warning icon next to it in the following areas of Dentrix Ascend: in the Enter payment dialog box, in the Enter credit adjustment dialog box, on the Payment tab of the Patient Walkout dialog box, and on the treatment plan case preview page. You can click a warning icon to view the details of the exception for the corresponding procedure.

-
You can add exceptions in a coverage table that is attached to an insurance plan.
To add an exception
-
On the Settings menu, under Production, click (or tap) Coverage Tables.
The Coverage Table Setup page opens.

-
Select a coverage table template.
The options for editing the coverage table appear.

-
Click (or tap) Manage Exceptions.

The Manage Exceptions dialog box appears.

-
Click (or tap) Add New Exception.
The New Exception for Procedure(s) dialog box appears.

-
Set up the options on the following tabs as needed:
-
Exception Type
-
Select one of the following options:
-
Not covered - To add procedures that are not covered.

-
Frequency - To add procedures that are covered at certain intervals.

-
Downgrade - To add a procedure that requires a downgrade.

-
Age limitation - To add procedures that have an age limitation.

-
-
Click (or tap) Next.
-
-
Select Procedure(s)
-
Do one of the following:
-
For a "Not covered" exception type, select the checkboxes that correspond to the procedure codes that are not covered.

Notes:
-
Only the procedure codes that do not have any exceptions are available for selection.
-
To quickly select or clear all checkboxes, select or clear the checkbox in the header at the top of the list.
-
To quickly select or clear a range of checkboxes, click (or tap) the first checkbox of the desired range, and then, while pressing the Shift key, click (or tap) the last checkbox of the desired range.
-
-
For a "Frequency" exception type, select the checkboxes that correspond to the procedure codes that are covered at certain intervals.

Notes:
-
Only the procedure codes that do not have a "Not covered" or "Frequency" exception are available for selection.
-
To quickly select or clear all checkboxes, select or clear the checkbox in the header at the top of the list.
-
To quickly select or clear a range of checkboxes, click (or tap) the first checkbox of the desired range, and then, while pressing the Shift key, click (or tap) the last checkbox of the desired range.
-
-
For a "Downgrade" exception type, select the procedure code that requires a downgrade.

Note: Only the procedure codes that do not have a "Not covered" or "Downgrade" exception are available for selection.
-
For an "Age limitation" exception type, select the checkboxes that correspond to the procedure codes that have an age limitation.

Notes:
-
Only the procedure codes that do not have a "Not covered" or "Age limitation" exception are available for selection.
-
To quickly select or clear all checkboxes, select or clear the checkbox in the header at the top of the list.
-
To quickly select or clear a range of checkboxes, click (or tap) the first checkbox of the desired range, and then, while pressing the Shift key, click (or tap) the last checkbox of the desired range.
-
Notes:
-
To search for a procedure, begin entering the code or its description in the Search for procedure box, continue typing as needed to narrow down the procedure code list.
-
After searching for and selecting a procedure, to return to viewing the entire procedure code list, delete the search text from the Search for procedure box.
-
-
Click (or tap) Next.
-
-
Specify Options
-
Do one of the following:
-
For a "Not covered" exception type, there are no options on this tab.

-
For a "Frequency" exception type, specify how often the insurance carrier covers this procedure within a given time period. For How many times, either enter a number, or click (or tap) + or - to change the number. For Over the course of, enter a number, and then select Year(s), Month(s), or Day(s) from the list.

Notes:
-
When you treatment plan a selected procedure for this exception, Dentrix Ascend takes the specified frequency limitation and the procedure date and coverage start date into account when it calculates an insurance estimate. For example, if procedure A was performed one year ago, and there is a once-every-two-years frequency limitation allowed by insurance for procedure A, if you treatment plan procedure A today, Dentrix Ascend looks back two years from today (assuming the start date of the patient’s insurance plan coverage is at least that far back) and recognizes that the previous posting of procedure A was rendered less than two years ago, so today’s planning of procedure A is seen as not covered. In this case, the estimated insurance portion is calculated as $0.00.
-
However, if a treatment area (such as tooth, quadrant, or arch) applies to a selected procedure for this exception, when you treatment plan that procedure, Dentrix Ascend takes the specified frequency limitation and treatment area into account when it calculates an insurance estimate. For example, if procedure A for the UL quadrant was performed three months ago, and there is a yearly frequency limitation allowed by insurance for procedure A if it is performed on the same treatment area, if you treatment plan procedure A for the UR quadrant today, Dentrix Ascend recognizes that the previous posting of procedure A was rendered on a different treatment area from the treatment area for today’s planning of procedure A, so the correct estimated insurance portion is calculated instead of $0.00.
-
-
For a "Downgrade" exception type, in the Downgrade to search box, begin entering the code or description of the substitute procedure, continue typing as needed to narrow the results, and then select the correct code.

-
For an "Age limitation" exception type, set up the following options:
-
Age limitation - Enter a minimum age limit (as young as 0 years) and a maximum age limit (as old as 110+ years) to specify that the insurance carrier covers this procedure only for patients whose age is within the specified limit. Also, you can use the left slider to change the minimum age and the right slider to change the maximum age.
Note: If the patient's age is not within the specified limit, the percentage (%) or copayment ($) in the coverage table is used.
-
Coverage, % or Downgrade - Do one of the following:
-
Specify a coverage percentage - Select the Coverage, % option. In the box, enter the percentage of the fee charged that the insurance carrier covers for this procedure.

Note: The Coverage, % box is available only for coverage tables that are based on insurance coverage percentages.
-
Specify a downgrade - Select the Downgrade to option. In the Search for procedure box, begin entering the code or description of the substitute procedure, continue typing as needed to narrow the results, and then select the correct code.

-
-
Copayment, $ or Downgrade - Do one of the following:
-
Specify a copayment - Select the Copayment, $ option. Enter the co-pay that the patient pays for this procedure.

Note: The Copayment, $ box is available only for coverage tables that are based on fixed, patient copayments.
-
Specify a downgrade - Select the Downgrade to option. In the Search for procedure box, begin entering the code or description of the substitute procedure, continue typing as needed to narrow the results, and then select the correct code.

-
-
Deductible Type - If the patient must pay a deductible for this procedure, select this checkbox, and then select the correct type of deductible from the corresponding list.
Note: The Deductible Type checkbox is available only if the Coverage, % or Copayment, $ option is selected.
-
-
-
Click (or tap) Next.
-
-
Reason for Exception
In the box, enter the reason for the exception in coverage for this procedure.

-
-
Click (or tap) Done.
Note: This button is available only if the Reason for Exception tab is selected.
2. Insurance plans
Updating insurance plan information
Updating insurance plan information
You can update the information for an insurance plan attached to an insurance carrier that was added to your organization's database. Any changes made to a plan's information affect all patients covered by that plan.
Note: Updating insurance plans requires the "Edit Insurance Plans" security right. However, if you have not been granted the "Edit Insurance Plans" security right, you can select a Max allowable amount fee schedule for the plan if you have been granted the "Assign Fee Schedule to Plan" security right.
To update an insurance plan
-
On the Home menu, under Insurance, click (or tap) Carriers.
The Insurance Carriers page opens.
-
Select an insurance carrier.
Tip: To help you locate an insurance carrier quickly, in the Filter box, enter part or all of a carrier's name, plan/employer, or group number to filter the carrier list so that it displays only those carriers that match what you enter.

The options to edit the insurance carrier become available.

-
Under Plans/Employers, select an insurance plan.

Tip: To help you locate a plan quickly, in the Filter box, enter part or all of the plan/employer name or group number to filter the plan list so that it displays only those plans that match what you enter.
The options for editing the insurance plan become available.

-
Change the plan information, such as the name or address, as needed.
Set up the following options:
-
Plan/Employer Name - The name of the employer or insurance plan.
-
Group # - The group plan number.
-
Claim mailing address - The address where claims for the insurance plan are sent.
Notes:
-
If you click in the first box to change the street address, a list of matching addresses appears. If you remove the street address, and begin typing a different address, as you type, matching addresses appear; continue typing as needed to narrow down the results.
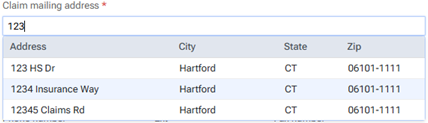
The list of matching addresses comes from the claim mailing addresses that have been entered across all the existing insurance plans in your organization's database.
-
Selecting an address updates the street address, city, state abbreviation, and ZIP Code for this plan accordingly.
-
If the correct address is not found, finish typing the street, and then specify the remaining parts of the address manually.
-
If you select an address, you can edit any part of the address as needed for this plan. Any changes that you make do not affect the addresses of any other plans.
-
-
ZIP Codes must be nine digits.
-
-
Phone - The insurance plan administrator's contact phone number and extension (if applicable).
-
Fax Number - The fax number of the insurance plan administrator.
-
Contact - The name of the insurance plan administrator.
-
Email - The insurance plan administrator's email address.
-
Benefit Renewal Month - The month that the insurance plan's benefits reset.
-
Source of Payment - The type of insurance company that will remit payment: CHAMPUS, Blue Cross/Blue Shield, Commercial Insurance, Commercial Insurance (PPO), Commercial Insurance (DHMO), Medicare Part B, or Medicaid.
-
Type - The plan covers dental or medical procedures.
-
Missing tooth clause? - Indicates if a missing tooth clause applies to the plan. Select one of the following options: Not Specified, Yes, or No.
Note: Currently, this option is for reference only.
-
Eligibility coverage level - Indicates the type of coverage that applies to the plan. Select one of the following options: Not Specified, Individual, Family, Employee Only, Employee and Spouse, Employee and Children, Spouse Only, Spouse and Children, Children Only, or Dependents Only.
Note: Currently, this option is for reference only.
-
Crowns/Bridges paid on - Indicates if the plan guidelines base payment on the preparation or seat date for procedures such as crowns and bridges. Select one of the following options: Not Specified, Prep Date, or Seat Date.
Note: Currently, this option is for reference only.
-
Max allowable amount fee schedule - The schedule of allowed charges for the insurance plan (PPO or DHMO plan only). The selected fee schedule will be used to determine a patient's portion and the recommended write-off.
Important: For each provider (and each location that is set up as a billing provider for claims) who participates with this insurance plan, in that provider's user account (or that location's settings), you must select this carrier in the Contracted With section.
Note: When you expand the list, you can use the search box at the top to quickly locate a fee schedule. Begin typing part of a fee schedule name in the box to see the matching fee schedules in the list. Continue typing as needed to narrow down the results. Select the correct fee schedule.
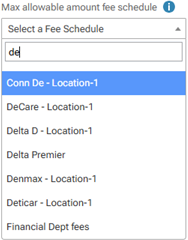
You can also click (or tap) Max Allowable All Locations to open the Max Allowable Amount Fee Schedules By Location dialog box and set the max allowable fee schedule for the insurance plan by location.

-
Coverage Table - The coverage table for the plan. Click (or tap) Coverage Table to open the Coverage Table for dialog box.

For a coverage table that is based on insurance coverage percentages, change the default deductible type and/or coverage percentage for each procedure code range. For a coverage table that is based on fixed, patient copayments, change the default deductible type and/or copayment amount.
Note: You can also add, edit, or delete exceptions to the coverage for specific procedures.
-
Benefits - The required deductibles and maximum benefits for the plan. Click (or tap) Benefits to open the Deductible and Benefits dialog box.

Enter the required deductible amounts for each deductible type, enter the maximum benefits allowed, and then click (or tap) Save.
Note: Adding required deductibles and maximum benefits to insurance plans requires the "Edit Benefits" security right.
-
Payment Table - The payment table for the plan. Click (or tap) Payment Table to open the Payment Table dialog box.

Manually add, edit, and remove procedures in the plan's payment table as needed.
-
Coordination of Benefits - The methods for handling the Coordination of Benefits (COB) between primary and secondary insurance claims for a patient with this insurance plan as his or her secondary plan. Click (or tap) Coordination of Benefits to open the Coordination of Benefits for dialog box.

For each Source of Payment for Primary Insurance Plan, select a Method for Coordination of Benefits, and then click (or tap) Save.
Notes:
-
If this insurance plan is attached to a patient's record as a secondary plan, the method being used for coordinating benefits appears on the patient's Insurance Information page when the options for the secondary plan are being displayed.

-
For more information about the coordination of benefits, refer to the topic about Coordination of benefits.
-
Changing the coordination of benefits for insurance plans requires the "Edit Insurance Plans" security right.
-
-
Predeterminations - The procedures that require a predetermination (pre-authorization) under this plan. Click (or tap) Predeterminations to open the Manage Predeterminations dialog box.

Do any of the following:
-
Select checkboxes:
-
To select the checkboxes of the listed procedures that commonly require a predetermination, click (or tap) Load Defaults. Be aware that doing this replaces the current selections.
-
To select the checkboxes of the listed procedures according to the selections from another insurance plan, enter your search criteria (part of a carrier name, plan/employer name, or group number) in the Replace with box, continue typing as needed to narrow the results, and then select the correct plan. Be aware that doing this replaces the current selections.
-
Manually select or clear the checkboxes of procedures in the list as needed.
Note: To quickly locate a procedure, begin entering part of its code, description, or treatment area in the Search for procedure box. The procedures that match your search criteria are listed. Continue typing as needed to narrow the results.
-
-
Set a charge threshold - To require a predetermination for any procedure that is not selected in the list but whose charge equals or exceeds a certain amount, select the Require predetermination for procedures over checkbox, and then enter an amount in the box provided.
-
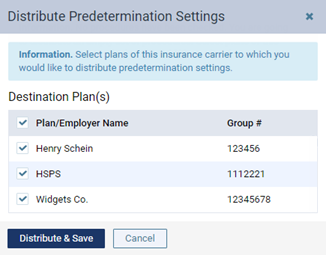
Copy selections to other plans - To copy this plan's selections to other plans that are associated with this plan's carrier, click (or tap) Distribute Settings. In the Distribute Predetermination Settings dialog box, select the checkboxes of the correct plans, and then click (or tap) Distribute & Save. Be aware that doing this replaces the current selections for the destination plans.
-
-
Note - A note that is specific to this insurance plan. You can enter text, such as information from an EOB or other document from the insurance carrier. Also, you can insert a date if needed. The note is accessible from all patient records that have this insurance plan attached.
-
-
Click (or tap) Save.
Editing coverage tables
Editing coverage tables
You can edit the coverage table that is attached to an insurance plan. A coverage table references the procedures that a carrier covers and either the percentage covered or the patient copayment. Along with deductibles and benefits, a coverage table allows for accurate insurance estimates.
Tip: You can also replace the coverage table of any given insurance plan with the coverage table from any other plan or from a coverage table template.
Important:
-
Changing an insurance plan's coverage table affects all patients who are covered by that insurance plan.
-
Changing a plan's coverage does not update the fees that are associated with treatment-planned procedures. You must either edit the fees manually for the procedures in a treatment plan case or delete and re-create the case and procedures.
To edit a coverage table
-
On the Home menu, under Insurance, click (or tap) Carriers.
The Insurance Carriers page opens.
-
Select an insurance carrier.
The options for editing the insurance carrier become available.
-
Under Plans/Employers, select an insurance plan.
The options for editing the insurance plan become available.
-
Click (or tap) Coverage Table.

The Coverage Table dialog box appears.

Insurance Coverage, %

Patient Copayment, $
-
If necessary, you can change the type of coverage table. From the Type list, select either Insurance Coverage, % or Patient Copayment, $ to specify whether the coverage should be based on a percentage or a fixed amount, respectively.

Notes:
-
If you change the type from Insurance Coverage, % to Patient Copayment, $, the coverage table changes to either the previous version of the patient copayment ($) type coverage table for this plan or, if this is the first time that you have changed the type, the default patient copayment ($) type coverage table.
-
If you change the type from Patient Copayment, $ to Insurance Coverage, %, the coverage table changes to either the previous version of the insurance coverage (%) type coverage table for this plan or, if this is the first time that you have changed the type, the default insurance coverage (%) type coverage table.
-
-
If necessary, you can replace the coverage table with that of a template or another plan, or you can delete the coverage table to make a new one from scratch (not recommended).
-
Do one of the following:
-
For an Insurance Coverage, % table, add, edit, and delete the procedure code ranges as needed.
Do the following:
-
Click (or tap) Add Range to add a procedure code range, or select an existing range to edit that range.

-
Set up the following options for that range as needed:
-
Code Range - The ADA or custom procedure code range. These boxes accept dashes (-), periods (.), numbers, and letters, and they can be up to 10 characters in length. Make sure there are not any overlaps and gaps in the sequence between the starting and ending codes in the range and between other ranges.
You can include an alias procedure codes in a range by typing a period (.) in either box. The Code Range boxes change to allow for entering suffixes. Enter a suffix in either or both suffix boxes. If you need a period in either of the main code boxes (the boxes to the left of the suffix boxes), you must type the period again in that box.

Note: When you change a range and then click (or tap) somewhere else, the text of the range that you modified turns bold. Also, any ranges that overlap or that are invalid become highlighted in red, and you cannot save the changes to the coverage table until those errors are resolved.
-
Category - The procedure category for the procedures in the range.
-
Deductible Type - The type of deductible that the procedures in the range apply to.
-
Coverage % - The percent that the insurance carrier pays on covered charges (after any deductible, up to any allowed amount, and up to any maximum allowed benefit) for procedures in the range.
-
-
Repeat the steps a - b for any other ranges that you want to add or edit.
-
To delete a range, click (or tap) the corresponding Remove button
 , and then click (or tap) Delete on the confirmation message that appears.
, and then click (or tap) Delete on the confirmation message that appears.Important: If you are deleting the only range in the coverage table, the entire table will be deleted.
-
-
For a Patient Copayment, $ table, add, edit, and delete the procedure codes as needed.
Do the following:
-
To add procedures codes, do the following:
-
Click (or tap) Add Procedure.

The Add Procedures dialog box appears.

-
Select the check boxes of the procedure codes that you want to add to the coverage table. You can select or deselect the check box in the column header to select and deselect all the procedure codes at the same time.
-
Click (or tap) Add Checked.
Note: If you are adding procedure codes to a coverage table that already has procedure codes, the procedure codes are added at the top of the table, which might not be the correct order; however, when you save the template, the procedure codes will be listed in the correct order.
-
-
To edit an existing or newly-added procedure code, select it.

-
Set up the following options for that code as needed:
-
Deductible Type - The type of deductible that the procedure applies to.
-
Copayment $ - The patient co-pay. Patients will pay the specified amount for the procedure.
-
-
Repeat the steps a - c for any other codes that you want to add or edit.
-
To delete a code, click (or tap) the corresponding Remove button
 , and then click (or tap) Delete on the confirmation message that appears.
, and then click (or tap) Delete on the confirmation message that appears.Important: If you are deleting the only code in the coverage table, the entire table will be deleted.
-
-
-
To add, edit, or delete exceptions to the coverage for specific procedures, click (or tap) Manage Exceptions.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To apply the changes to the coverage table and create a new coverage table template using the specified coverage options, click (or tap) Save As New Template. In the New Coverage Table Template dialog box that appears, enter a name for the template, and then click (or tap) Save.

-
To apply the changes to the coverage table, click (or tap) Save.
-
-
Click (or tap) Save or Cancel.
Editing exceptions in coverage tables
Editing exceptions in coverage tables
You can edit exceptions that have been added previously to a coverage table that is attached to an insurance plan.
Important:
-
The exceptions in coverage tables of the type "Insurance Coverage, %" are used by Dentrix Ascend to automatically calculate insurance estimates.
-
The exceptions in coverage tables of the type "Patient Copayment, $" are not used by Dentrix Ascend to automatically calculate insurance estimates.
Notes:
-
If a patient has dual coverage, the exceptions of the primary insurance coverage are used.
-
A posted procedure with an exception will have a warning icon next to it in the following areas of Dentrix Ascend: in the Enter payment dialog box, in the Enter credit adjustment dialog box, on the Payment tab of the Patient Walkout dialog box, and on the treatment plan case preview page. You can click a warning icon to view the details of the exception for the corresponding procedure.

-
Editing exceptions in an insurance plan's coverage table requires the "Edit Insurance Plans" security right.
-
You can also edit exceptions in any of the coverage table templates.
To edit an exception
-
On the Home menu, under Insurance, click (or tap) Carriers.
The Insurance Carriers page opens.
-
Select an insurance carrier.
The options for editing the insurance carrier become available.
-
Under Plans/Employers, select an insurance plan.
The options for editing the insurance plan become available.
-
Click (or tap) Coverage Table.

The Coverage Table dialog box appears.

-
Click (or tap) Manage Exceptions.

The Manage Exceptions dialog box appears.

-
In the Exceptions list, expand a Code to view the corresponding exceptions, and then select an exception.
Notes:
-
To search for a procedure code, begin entering a code in the Search for a procedure by code box, and continue typing as needed to narrow the list.
-
If at least one Code is expanded, to quickly collapse them all, click (or tap) Collapse All. If they are all collapsed, to expand them all, click (or tap) Expand All.
The Edit Exception dialog box appears.

-
-
Set up the options on the following tabs as needed:
-
Exception Type
-
Select one of the following options:
-
Not covered - To add procedures that are not covered.

-
Frequency - To add procedures that are covered at certain intervals.

-
Downgrade - To add a procedure that requires a downgrade.

-
Age limitation - To add procedures that have an age limitation.

-
Waiting Period - To add procedures that have a waiting period.
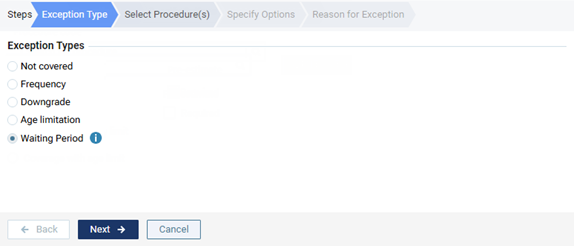
Note: Currently, this exception type is for reference purposes only and not used for insurance estimate calculations.
-
-
Click (or tap) Next.
-
-
Select Procedure(s)
-
Do one of the following:
-
For a "Not covered" exception type, select the check boxes that correspond to the procedure codes that are not covered.

Notes:
-
Only the procedure codes that do not have any exceptions are available for selection.
-
To quickly select or clear all check boxes, select or clear the check box in the header at the top of the list.
-
To quickly select or clear a range of check boxes, click (or tap) the first check box of the desired range, and then, while pressing the Shift key, click (or tap) the last check box of the desired range.
-
-
For a "Frequency" exception type, select the checkboxes that correspond to the procedure codes that are covered at certain intervals.

Notes:
-
Only the procedure codes that do not have a "Not covered" exception are available for selection.
-
If a "Frequency" exception already exists for a selected procedure, with that procedure's checkbox selected for this new exception, the existing "Frequency" exception for that procedure will be replaced with this new exception.
-
To quickly select or clear all checkboxes, select or clear the checkbox in the header at the top of the list.
-
To quickly select or clear a range of checkboxes, click (or tap) the first checkbox of the desired range, and then, while pressing the Shift key, click (or tap) the last checkbox of the desired range.
-
-
For a "Downgrade" exception type, select the procedure code that requires a downgrade.

Note: Only the procedure codes that do not have a "Not covered" or "Downgrade" exception are available for selection.
-
For an "Age limitation" exception type, select the check boxes that correspond to the procedure codes that have an age limitation.

Notes:
-
Only the procedure codes that do not have a "Not covered" exception are available for selection.
-
If an "Age limitation" exception already exists for a selected procedure, with that procedure's checkbox selected for this new exception, the existing "Age limitation" exception for that procedure will be replaced with this new exception.
-
To quickly select or clear all check boxes, select or clear the check box in the header at the top of the list.
-
To quickly select or clear a range of check boxes, click (or tap) the first check box of the desired range, and then, while pressing the Shift key, click (or tap) the last check box of the desired range.
-
-
For a "Waiting Period" exception type, select the checkboxes that correspond to the procedure codes that have a waiting period.
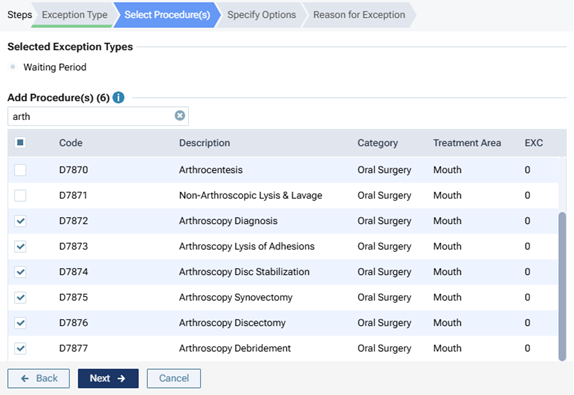
Notes:
-
Only the procedure codes that do not have a "Not covered" exception are available for selection.
-
If a "Waiting Period" exception already exists for a selected procedure, with that procedure's checkbox selected for this new exception, the existing "Waiting Period" exception for that procedure will be replaced with this new exception.
-
To quickly select or clear all checkboxes, select or clear the checkbox in the header at the top of the list.
-
To quickly select or clear a range of checkboxes, click (or tap) the first checkbox of the desired range, and then, while pressing the Shift key, click (or tap) the last checkbox of the desired range.
-
Notes:
-
To search for a procedure, begin entering the code or its description in the Search for procedure box, continue typing as needed to narrow down the procedure code list.
-
After searching for and selecting a procedure, to return to viewing the entire procedure code list, delete the search text from the Search for procedure box.
-
-
Click (or tap) Next.
-
-
Specify Options
-
Do one of the following:
-
For a "Not covered" exception type, there are no options on this tab.

-
For a "Frequency" exception type, specify how often the insurance carrier covers this procedure within a given time period. For How many times, either enter a number, or click (or tap) + or - to change the number. For Over the course of, enter a number, and then select Year(s), Month(s), or Day(s) from the list.

Notes:
-
When you treatment plan a selected procedure for this exception, Dentrix Ascend takes the specified frequency limitation and the procedure date and coverage start date into account when it calculates an insurance estimate. For example, if procedure A was performed one year ago, and there is a once-every-two-years frequency limitation allowed by insurance for procedure A, if you treatment plan procedure A today, Dentrix Ascend looks back two years from today (assuming the start date of the patient’s insurance plan coverage is at least that far back) and recognizes that the previous posting of procedure A was rendered less than two years ago, so today’s planning of procedure A is seen as not covered. In this case, the estimated insurance portion is calculated as $0.00.
-
However, if a treatment area (such as tooth, quadrant, or arch) applies to a selected procedure for this exception, when you treatment plan that procedure, Dentrix Ascend takes the specified frequency limitation and treatment area into account when it calculates an insurance estimate. For example, if procedure A for the UL quadrant was performed three months ago, and there is a yearly frequency limitation allowed by insurance for procedure A if it is performed on the same treatment area, if you treatment plan procedure A for the UR quadrant today, Dentrix Ascend recognizes that the previous posting of procedure A was rendered on a different treatment area from the treatment area for today’s planning of procedure A, so the correct estimated insurance portion is calculated instead of $0.00.
-
-
For a "Downgrade" exception type, in the Downgrade to search box, begin entering the code or description of the substitute procedure, continue typing as needed to narrow the results, and then select the correct code.

-
For an "Age limitation" exception type, set up the following options:
-
Age limitation - Enter a minimum age limit (as young as 0 years) and a maximum age limit (as old as 110+ years) to specify that the insurance carrier covers this procedure only for patients whose age is within the specified limit. Also, you can use the left slider to change the minimum age and the right slider to change the maximum age.
Note: If the patient's age is not within the specified limit, the percentage (%) or copayment ($) in the coverage table is used.
-
Coverage, % or Downgrade - Do one of the following:
-
Specify a coverage percentage - Select the Coverage, % option. In the box, enter the percentage of the fee charged that the insurance carrier covers for this procedure.

Note: The Coverage, % box is available only for coverage tables that are based on insurance coverage percentages.
-
Specify a downgrade - Select the Downgrade to option. In the Search for procedure box, begin entering the code or description of the substitute procedure, continue typing as needed to narrow the results, and then select the correct code.

-
-
Copayment, $ or Downgrade - Do one of the following:
-
Specify a copayment - Select the Copayment, $ option. Enter the co-pay that the patient pays for this procedure.

Note: The Copayment, $ box is available only for coverage tables that are based on fixed, patient copayments.
-
Specify a downgrade - Select the Downgrade to option. In the Search for procedure box, begin entering the code or description of the substitute procedure, continue typing as needed to narrow the results, and then select the correct code.

-
-
Deductible Type - If the patient must pay a deductible for this procedure, select this check box, and then select the correct type of deductible from the corresponding list.
Note: The Deductible Type check box is available only if the Coverage, % or Copayment, $ option is selected.
-
-
For a "Waiting Period" exception type, specify the length of the waiting period that is required for the insurance carrier to cover this procedure. For the box, either enter a number, or click (or tap) + or - to change the number. From the list, select Year(s), Month(s), Week(s) or Day(s) from the list.
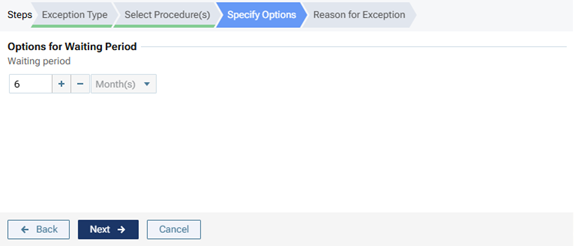
Note: Currently, this exception type is for reference purposes only and not used for insurance estimate calculations.
-
-
Click (or tap) Next.
-
-
Reason for Exception
In the box, enter the reason for the exception in coverage for this procedure.

-
-
Click (or tap) Done.
Note: This button is available only if the Reason for Exception tab is selected.
3. Insurance estimates
Understanding how insurance estimates are calculated
Understanding how insurance estimates are calculated
Dentrix Ascend calculates insurance portions, write-off adjustments, and patient portions automatically. The explanation that follows covers estimates for primary and secondary plans. The same rules and calculations that apply to secondary plans apply to plans for other coverage orders (tertiary, quaternary, and so forth); however, the calculations are not performed automatically.
The commercial insurance plans that Dentrix Ascend supports are PPO (Preferred Provider Organization), DHMO (Dental Health Maintenance Organization), and indemnity.
Notes:
-
Before calculating insurance estimates for procedures posted on the current date, Dentrix Ascend takes into account any pending primary and secondary claims (in the order they were sent, and claims with the highest total billed amount being handled first) for the patient, the subscriber of the patient's plan (if not the same person), and any other dependents on the plan. However, insurance estimates do not take into account a tertiary plan unless a claim for that plan is attached to a secondary claim; likewise, estimates do not take into account a quaternary plan unless a claim for that plan is attached to a tertiary claim; and so forth.
-
Dentrix Ascend processes procedures being billed to insurance chronologically (oldest to newest, by procedure dates), by descending procedure predetermination or override amounts (largest to smallest), and then by descending procedure amounts (largest to smallest).
-
When calculating estimates for an insurance payment, Dentrix Ascend processes only the procedures associated with the current claim. The maximums and deductibles are calculated as if the current claim is the next one to be paid.
-
For Dentrix Ascend to calculate estimates for procedures posted on the current date, the patient must have an active primary insurance plan with coverage dates that include the dates of those posted procedures.
-
Estimates include procedures posted on the current date and prior, even if those procedures are not attached to a claim.
-
The deductible type for multiple procedures posted on the same date is determined by the first procedure.
-
The billing provider, which is determined by the insurance defaults, may be different from the provider who is associated with a procedure.
-
Patient payments and credit adjustments that are applied to procedures reduce the estimated patient portion. Insurance payments that are less than what is expected to be paid reduce the estimated insurance portion and increase the estimated patient portion. Partial insurance payments (more is expected to be paid) reduce the estimated insurance portion.
Estimates for a patient's primary or only insurance plan
Do the following:
-
Calculate the Write-off.
Terms
W
Write-off
Aproc
Amount Charged (the procedure's Amount)
Amax
Max Allowable Amount (from the plan's Max allowable amount fee schedule)
Apay
Payment Table Amount (from the Amount column in the plan's payment table)
Cpat
Patient Copay (from the Copayment $ column in the plan's coverage table)
Do one of the following:
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is selected for the plan, do one of the following:
-
If the billing provider is contracted with the carrier, do one of the following:
-
For a coverage table based on patient copayments ($), take the greater of Amax and Cpat, subtract that greater amount from Aproc, and then set W equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set W equal to zero.
W = max (0 ; Aproc - max (Amax ; Cpat))
-
For a coverage table based on insurance coverage percentages (%), do one of the following:
-
If a procedure is listed in the payment table, take the greater of Amax and Apay, subtract that greater amount from Aproc, and then set W equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set W equal to zero.
W = max (0 ; Aproc - max (Amax ; Apay))
-
If a procedure is not listed in the payment table, subtract Amax from Aproc, and then set Wpri equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Wpri equal to zero.
W = max (0 ; Aproc - Amax)
-
-
-
If the billing provider is not contracted with the carrier, set W equal to zero.
W = 0
-
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is not selected for the plan, there is not a Write-off, so set W equal to zero.
W = 0
-
-
Calculate the Remaining Deductible.
Term
Drem
Remaining Deductible
Note: No value or a zero (0) for a required deductible both indicate that no deductible is required.
-
Do one of the following:
-
For an orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
Calculate the Remaining Annual Individual Ortho Deductible:
Terms
AIODreq
Required Annual Individual Ortho Deductible
AIODmet
Met Annual Individual Ortho Deductible
AIODrem
Remaining Annual Individual Ortho Deductible
-
If AIODreq has no value, then AIODrem = 0
-
If AIODreq = 0, then AIODrem = 0
-
If AIODreq > 0, then AIODrem = AIODreq - AIODmet
-
-
Set the Remaining Deductible (Drem) equal to the Remaining Annual Individual Ortho Deductible (AIODrem).
Drem = AIODrem
-
-
For a non-orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
For the Lifetime Individual Deductible, calculate the Remaining Lifetime Individual Deductible:
Terms
LIDreq
Required Lifetime Individual Deductible
LIDmet
Met Lifetime Individual Deductible
LIDrem
Remaining Lifetime Individual Deductible
-
If LIDreq has no value, then LIDrem = 0
-
If LIDreq = 0, then LIDrem = 0
-
If LIDreq > 0, then LIDrem = LIDreq - LIDmet
-
-
For the Annual Family Deductible, calculate the Remaining Annual Family Deductible:
Terms
AFDreq
Required Annual Family Deductible
AFDmet
Met Annual Family Deductible
AFDrem
Remaining Annual Family Deductible
-
If AFDreq has no value, then AFDrem = 0
-
If AFDreq = 0, then AFDrem = 0
-
If AFDreq > 0, then AFDrem = AFDreq - AFDmet
-
-
For the Annual Individual Deductible, calculate the Remaining Annual Individual Deductible:
Terms
AIDreq
Required Annual Individual Deductible
AIDmet
Met Annual Individual Deductible
AIDrem
Remaining Annual Individual Deductible
-
If AIDreq has no value, then AIDrem = 0
-
If AIDreq = 0, then AIDrem = 0
-
If AIDreq > 0, then AIDrem = AIDreq - AIDmet
-
-
Calculate the Remaining Deductible. Take the lesser of LIDrem, AFDrem, and AIDrem, and set Drem equal to that lesser amount.
Drem = min (LIDrem ; AFDrem ; AIDrem)
-
-
-
-
Calculate the Insurance Portion.
Terms
I
Insurance Portion
Aproc
Amount Charged (the procedure's Amount)
Amax
Max Allowable Amount (from the plan's Max allowable amount fee schedule)
Amin
Min Allowable Amount
Apay
Payment Table Amount (from the Amount column in the plan's payment table)
Cpat
Patient Copay (from the Copayment $ column in the plan's coverage table)
Cins
Insurance Coverage Percentage (from the Coverage % column in the plan's coverage table)
Cexc
Patient Copay Exception or Insurance Coverage Exception (any applicable exceptions, as indicated in the EXC column, in the plan's coverage table)
Oins
Insurance Estimate Override (from the procedure's Insurance Estimate Overrides; entered and locked automatically, or entered manually)
Do one of the following:
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is selected for the plan, do the following:
-
Calculate the Min Allowable. Because the calculations for the Insurance Portion require that Amax not exceed Aproc, take the lesser of Aproc and Amax, and then set Amin equal to that lesser amount.
Amin = min (Aproc ; Amax)
-
Calculate the Insurance Portion. Do one of the following:
-
Without an Insurance Estimate Override, do one of the following:
-
For a coverage table based on patient copayments, do the following:
-
Determine the Patient Copay. Do one of the following:
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, it is ignored currently. Use the default copay.
Cpat = Cpat
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default copay.
Cpat = Cpat
-
-
Calculate the Insurance Portion. Subtract Cpat from Amin, and then set I equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set I equal to zero.
I = max (0 ; Amin - Cpat)
-
-
For a coverage table based on insurance coverage percentages, do one of the following:
-
If a procedure is listed in the payment table, take the greater of Amin and Apay, and then set I equal to that greater amount.
I = max (Amin ; Apay)
-
If a procedure is not listed in the payment table, do the following:
-
Determine the Insurance Coverage Percentage. Do one of the following:
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use one of the following exception types to determine the coverage:
-
Not covered. The carrier does not have a portion, so set Cins equal to zero.
Cins = 0
-
Frequency. Do one of the following:
-
For a procedure with a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, do one of the following:
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for the same treatment area, set Cins equal to zero.
Cins = 0
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for a different treatment area, use the default coverage.
Cins = Cins
-
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set Cins equal to zero
Cins = 0
-
-
For a procedure without a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, use the default coverage.
Cins = Cins
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set Cins equal to zero.
Cins = 0
-
-
-
Downgrade. Use the exception instead of the default coverage.
Cins = Cexc
-
Age limitation. Do one of the following:
-
If the patient's age does not exceed the specified age, use the exception instead of the default coverage.
Cins = Cexc
-
If the patient's age exceeds the specified age, use the default coverage.
Cins = Cins
-
-
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default coverage.
Cins = Cins
-
-
Calculate the Insurance Portion. Multiply Amin and Cins, and then set I equal to that product unless that product is less than zero, in which case, set I equal to zero.
I = max (0 ; Amin x Cins)
-
-
-
-
With an Insurance Estimate Override, take the greater of Oins and Amin, and then set I equal to that greater amount unless that greater amount is less than zero, in which case, set I equal to zero.
I = max (0 ; min (Oins ; Amin))
-
-
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is not selected for the plan, do one of the following:
-
Without an Insurance Estimate Override, do one of the following:
-
For a coverage table based on patient copayments, do the following:
-
Determine the Patient Copay. Do one of the following:
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, it is ignored currently. Use the default copay.
Cpat = Cpat
-
-
Calculate the Insurance Portion. Subtract Cpat from Aproc, and then set I equal to that difference.
I = Aproc - Cpat
-
-
For a coverage table based on insurance coverage percentages, do one of the following:
-
If a procedure is listed in the payment table, set I equal to Apay.
I = Apay
-
If a procedure is not listed in the payment table, do the following:
-
Determine the Insurance Coverage Percentage. Do one of the following:
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use one of the following exception types to determine the coverage:
-
Not covered. The carrier does not have a portion, so set Cins equal to zero.
Cins = 0
-
Frequency. Do one of the following:
-
For a procedure with a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, do one of the following:
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for the same treatment area, set Cins equal to zero.
Cins = 0
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for a different treatment area, use the default coverage.
Cins = Cins
-
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set Cins equal to zero
Cins = 0
-
-
For a procedure without a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, use the default coverage.
Cins = Cins
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set Cins equal to zero.
Cins = 0
-
-
-
Downgrade. Use the exception instead of the default coverage.
Cins = Cexc
-
Age limitation. Do one of the following:
-
If the patient's age does not exceed the specified age, use the exception instead of the default coverage.
Cins = Cexc
-
If the patient's age exceeds the specified age, use the default coverage.
Cins = Cins
-
-
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default coverage.
Cins = Cins
-
-
Calculate the Insurance Portion. Multiply Aproc and Cins, and then set I equal to that product.
I = Aproc x Cins
-
-
-
-
With an Insurance Estimate Override, set I equal to the override.
I = Oins
-
-
-
Calculate the Patient Portion.
Terms
P
Patient Portion
Aproc
Amount Charged (the procedure's Amount)
I
Insurance Portion
W
Write-off
Subtract I and W from Aproc, and then set P equal to that difference.
P = Aproc - I - W
-
Use the Remaining Deductible to adjust the Insurance Portion and the Patient Portion as needed.
Terms
I
Insurance Portion
P
Patient Portion
Drem
Remaining Deductible
Do the following:
-
Subtract Drem from I, and then set I equal to that difference.
I = I - Drem
-
Add P and Drem, and then set P equal to that sum.
P = P + Drem
-
-
Calculate the Remaining Benefit.
Term
Brem
Remaining Benefit
Note: No value for a maximum indicates unlimited benefits; zero (0) indicates no benefits.
Do one of the following:
-
For an orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
Calculate the Remaining Lifetime Ortho Benefit:
Terms
LOBmax
Maximum Lifetime Ortho Benefit
LOBused
Used Lifetime Ortho Benefit
LOBrem
Remaining Lifetime Ortho Benefit
-
If LOBmax has no value, then LOBrem = 9,999,999.99
-
If LOBmax = 0, then LOBrem = 0
-
If LOBmax > 0, then LOBrem = LOBmax - LOBused
-
-
Set the Remaining Benefit (Brem) equal to the Remaining Lifetime Ortho Benefit (LOBrem).
Brem = LOBrem
-
-
For a non-orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
Calculate the Remaining Annual Individual Benefit:
Terms
AIBmax
Maximum Annual Individual Benefit
AIBused
Used Annual Individual Benefit
AIBrem
Remaining Annual Individual Benefit
-
If AIBmax has no value, then AIBrem = 9,999,999.99
-
If AIBmax = 0, then AIBrem = 0
-
If AIBmax > 0, then AIBrem = AIBmax - AIBused
-
-
Calculate the Remaining Annual Family Benefit:
Terms
AFBmax
Maximum Annual Family Benefit
AFBused
Used Annual Family Benefit
AFBrem
Remaining Annual Family Benefit
-
If AFBmax has no value, then AFBrem = 9,999,999.99
-
If AFBmax = 0, then AFBrem = 0
-
If AFBmax > 0, then AFBrem = AFBmax - AFBused
-
-
Calculate the Remaining Benefit. Take the lesser of AIBrem and AFBrem, and then set Brem equal to that lesser amount.
Brem = min (AIBrem ; AFBrem)
-
-
-
Use the Remaining Benefit to adjust the Insurance Portion and the Patient Portion as needed.
Terms
I
Insurance Portion
Brem
Remaining Benefit
P
Patient Portion
Bover
Benefit Overage
Recalculate the Insurance Portion and the Patient Portion. Do one of the following:
-
If I <= Brem, there is enough remaining benefit to cover the entire amount that is expected to be paid by the carrier.
-
The Insurance Portion does not change.
I = I
-
The Patient Portion does not change.
P = P
-
-
If I > Brem, the remaining benefits covers none or only a portion of the amount that is expected to be paid by the carrier, so do the following:
-
Calculate the Benefit Overage.
Bover = I - Brem
-
Recalculate the Insurance Portion. Set I equal to Brem.
I = Brem
-
Recalculate the Patient Portion. Add P and Bover, and then set P equal to that sum.
P = P + Bover
-
-
Estimates for dual coverage
Do the following:
-
Calculate the Primary Write-off.
Terms
Wpri
Primary Write-off
Aproc
Amount Charged (the procedure's Amount)
AP.max
Primary Max Allowable Amount (from the plan's Max allowable amount fee schedule)
AP.pay
Primary Payment Table Amount (from the Amount column in the plan's payment table)
CP.pat
Primary Patient Copay (from the Copayment $ column in the plan's coverage table)
Do one of the following:
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is selected for the plan, do one of the following:
-
If the billing provider is contracted with the carrier, do one of the following:
-
For a coverage table based on patient copayments ($), take the greater of AP.max and CP.pat, subtract that from Aproc, and then set Wpri equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Wpri equal to zero.
Wpri = max (0 ; Aproc - max (AP.max ; CP.pat))
-
For a coverage table based on insurance coverage percentages (%), do one of the following:
-
If a procedure is listed in the payment table, take the greater of AP.max and AP.pay, subtract that greater amount from Aproc, and then set Wpri equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set W equal to zero.
Wpri = max (0 ; Aproc - max (AP.max ; AP.pay))
-
If a procedure is not listed in the payment table, subtract AP.max from Aproc, and then set Wpri equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Wpri equal to zero.
Wpri = max (0 ; Aproc - AP.max)
-
-
-
If the billing provider is not contracted with the carrier, set Wpri equal to zero.
Wpri = 0
-
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is not selected for the plan, there is not a Primary Write-off, so set Wpri equal to zero.
Wpri = 0
-
-
Calculate the Secondary Write-off.
Terms
Wsec
Secondary Write-off
Aproc
Amount Charged (the procedure's Amount)
AS.max
Secondary Max Allowable Amount (from the plan's Max allowable amount fee schedule)
AS.pay
Secondary Payment Table Amount (from the Amount column in the plan's payment table)
CS.pat
Secondary Patient Copay (from the Copayment $ column in the plan's coverage table)
Do one of the following:
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is selected for the plan, do one of the following:
-
If the billing provider is contracted with the carrier, do one of the following:
-
For a coverage table based on patient copayments ($), take the greater of AS.max and CS.pat, subtract that from Aproc, and then set Wsec equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Wsec equal to zero.
Wsec = max (0 ; Aproc - max (AS.max ; CS.pat))
-
For a coverage table based on insurance coverage percentages (%), do one of the following:
-
If a procedure is listed in the payment table, take the greater of AS.max and AS.pay, subtract that greater amount from Aproc, and then set Wsec equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set W equal to zero.
Wsec = max (0 ; Aproc - max (AS.max ; AS.pay))
-
If a procedure is not listed in the payment table, subtract AS.max from Aproc, and then set Wsec equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Wsec equal to zero.
Wsec = max (0 ; Aproc - AS.max)
-
-
-
If the billing provider is not contracted with the carrier, set Wsec equal to zero.
Wsec = 0
-
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is not selected for the plan, there is not a Secondary Write-off, so set Wsec equal to zero.
Wsec = 0
-
-
Calculate the Max Write-off.
Terms
Wmax
Max Write-off
Wpri
Primary Write-off
Wsec
Secondary Write-off
Take the greater of Wpri and Wsec, and then set Wmax equal to that greater amount.
Wmax = max (Wpri ; Wsec)
-
Calculate the Primary Remaining Deductible.
Term
DP.rem
Primary Remaining Deductible
Note: No value or a zero (0) for a required deductible both indicate that no deductible is required.
-
Do one of the following:
-
For an orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
Calculate the Primary Remaining Annual Individual Ortho Deductible:
Terms
AIODP.req
Primary Required Annual Individual Ortho Deductible
AIODP.met
Primary Met Annual Individual Ortho Deductible
AIODP.rem
Primary Remaining Annual Individual Ortho Deductible
-
If AIODP.req has no value, then AIODP.rem = 0
-
If AIODP.req = 0, then AIODP.rem = 0
-
If AIODP.req > 0, then AIODP.rem = AIODP.req - AIODP.met
-
-
Set the Primary Remaining Deductible (DP.rem) equal to the Primary Remaining Annual Individual Ortho Deductible (AIODP.rem).
DP.rem = AIODP.rem
-
-
For a non-orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
For the Lifetime Individual Deductible, calculate the Primary Remaining Lifetime Individual Deductible:
Terms
LIDP.req
Primary Required Lifetime Individual Deductible
LIDP.met
Primary Met Lifetime Individual Deductible
LIDP.rem
Primary Remaining Lifetime Individual Deductible
-
If LIDP.req has no value, then LIDP.rem = 0
-
If LIDP.req = 0, then LIDP.rem = 0
-
If LIDP.req > 0, then LIDP.rem = LIDP.req - LIDP.met
-
-
For the Annual Family Deductible, calculate the Primary Remaining Annual Family Deductible:
Terms
AFDP.req
Primary Required Annual Family Deductible
AFDP.met
Primary Met Annual Family Deductible
AFDP.rem
Primary Remaining Annual Family Deductible
-
If AFDP.req has no value, then AFDP.rem = 0
-
If AFDP.req = 0, then AFDP.rem = 0
-
If AFDP.req > 0, then AFDP.rem = AFDP.req - AFDP.met
-
-
For the Annual Individual Deductible, calculate the Primary Remaining Annual Individual Deductible:
Terms
AIDP.req
Primary Required Annual Individual Deductible
AIDP.met
Primary Met Annual Individual Deductible
AIDP.rem
Primary Remaining Annual Individual Deductible
-
If AIDP.req has no value, then AIDP.rem = 0
-
If AIDP.req = 0, then AIDP.rem = 0
-
If AIDP.req > 0, then AIDP.rem = AIDP.req - AIDP.met
-
-
Calculate the Primary Remaining Deductible. Take the lesser of LIDP.rem, AFDP.rem, and AIDP.rem, and set DP.rem equal to that lesser amount.
DP.rem = min (LIDP.rem ; AFDP.rem ; AIDP.rem)
-
-
-
-
Calculate the Primary Insurance Portion.
Terms
Ipri
Primary Insurance Portion
Aproc
Amount Charged (the procedure's Amount)
AP.max
Primary Max Allowable Amount (from the plan's Max allowable amount fee schedule)
AP.min
Primary Min Allowable Amount
AP.pay
Primary Payment Table Amount (from the Amount column in the plan's payment table)
CP.pat
Primary Patient Copay (from the Copayment $ column in the plan's coverage table)
CP.ins
Primary Insurance Coverage Percentage (from the Coverage % column in the plan's coverage table)
CP.exc
Primary Patient Copay Exception or Primary Insurance Coverage Exception (any applicable exceptions, as indicated in the EXC column, in the plan's coverage table)
OP.ins
Primary Insurance Estimate Override (from the procedure's Insurance Estimate Overrides; entered and locked automatically, or entered manually)
Do one of the following:
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is selected for the plan, do the following:
-
Calculate the Primary Min Allowable. Because the calculations for the Primary Insurance Portion require that AP.max not exceed Aproc, take the lesser of Aproc and AP.max, and then set AP.min equal to that lesser amount.
AP.min = min (Aproc ; AP.max)
-
Calculate the Primary Insurance Portion. Do one of the following:
-
Without a Primary Insurance Estimate Override, do one of the following:
-
For a coverage table based on patient copayments, do the following:
-
Determine the Primary Patient Copay. Do one of the following:
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, it is ignored currently. Use the default copay.
CP.pat = CP.pat
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default copay.
CP.pat = CP.pat
-
-
Calculate the Primary Insurance Portion. Subtract CP.pat from AP.min, and then set Ipri equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Ipri equal to zero.
Ipri = max (0 ; AP.min - CP.pat)
-
-
For a coverage table based on insurance coverage percentages, do one of the following:
-
If a procedure is listed in the payment table, take the greater of AP.min and AP.pay, and then set Ipri equal to that greater amount.
Ipri = max (AP.min ; AP.pay)
-
If a procedure is not listed in the payment table, do the following:
-
Determine the Primary Insurance Coverage Percentage. Do one of the following:
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use one of the following exception types to determine the coverage:
-
Not covered. The carrier does not have a portion, so set CP.ins equal to zero.
CP.ins = 0
-
Frequency. Do one of the following:
-
For a procedure with a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, do one of the following:
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for the same treatment area, set CP.ins equal to zero.
CP.ins = 0
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for a different treatment area, use the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.ins
-
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set CP.ins equal to zero
CP.ins = 0
-
-
For a procedure without a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, use the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.ins
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set CP.ins equal to zero.
CP.ins = 0
-
-
-
Downgrade. Use the exception instead of the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.exc
-
Age limitation. Do one of the following:
-
If the patient's age does not exceed the specified age, use the exception instead of the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.exc
-
If the patient's age exceeds the specified age, use the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.ins
-
-
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.ins
-
-
Calculate the Primary Insurance Portion. Multiply AP.min and CP.ins, and then set Ipri equal to that product unless that product is less than zero, in which case, set Ipri equal to zero.
Ipri = max (0 ; AP.min x CP.ins)
-
-
-
-
With a Primary Insurance Estimate Override, take the greater of OP.ins and AP.min, and then set Ipri equal to that greater amount unless that greater amount is less than zero, in which case, set Ipri equal to zero.
Ipri = max (0 ; min (OP.ins ; AP.min))
-
-
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is not selected for the plan, do one of the following:
-
Without a Primary Insurance Estimate Override, do one of the following:
-
For a coverage table based on patient copayments, do the following:
-
Determine the Primary Patient Copay. Do one of the following:
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, it is ignored currently. Use the default copay.
CP.pat = CP.pat
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default copay.
CP.pat = CP.pat
-
-
Calculate the Primary Insurance Portion. Subtract CP.pat from Aproc, and then set Ipri equal to that difference.
Ipri = Aproc - CP.pat
-
-
For a coverage table based on insurance coverage percentages, do one of the following:
-
If a procedure is listed in the payment table, set Ipri equal to AP.pay.
Ipri = AP.pay
-
If a procedure is not listed in the payment table, do the following:
-
Determine the Primary Insurance Coverage. Do one of the following:
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use one of the following exception types to determine the coverage:
-
Not covered. The carrier does not have a portion, so set CP.ins equal to zero.
CP.ins = 0
-
Frequency. Do one of the following:
-
For a procedure with a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, do one of the following:
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for the same treatment area, set CP.ins equal to zero.
CP.ins = 0
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for a different treatment area, use the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.ins
-
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set CP.ins equal to zero
CP.ins = 0
-
-
For a procedure without a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, use the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.ins
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set CP.ins equal to zero.
CP.ins = 0
-
-
-
Downgrade. Use the exception instead of the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.exc
-
Age limitation. Do one of the following:
-
If the patient's age does not exceed the specified age, use the exception instead of the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.exc
-
If the patient's age exceeds the specified age, use the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.ins
-
-
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default coverage.
CP.ins = CP.ins
-
-
Calculate the Primary Insurance Portion. Multiply Aproc and CP.ins, and then set Ipri equal to that product.
Ipri = Aproc x CP.ins
-
-
-
-
With a Primary Insurance Estimate Override, set Ipri equal to the override.
Ipri = OP.ins
-
-
-
Use the Primary Remaining Deductible to set the Max Primary Insurance Portion.
Terms
IP.max
Max Primary Insurance Portion
Ipri
Primary Insurance Portion
DP.rem
Primary Remaining Deductible
Subtract DP.rem from Ipri, and then set IP.max equal to that difference.
IP.max = Ipri - DP.rem
-
Calculate the Primary Remaining Benefit.
Term
BP.rem
Primary Remaining Benefit
Note: No value for a maximum indicates unlimited benefits; zero (0) indicates no benefits.
Do one of the following:
-
For an orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
Calculate the Primary Remaining Lifetime Ortho Benefit:
Terms
LOBP.max
Primary Maximum Lifetime Ortho Benefit
LOBP.used
Primary Used Lifetime Ortho Benefit
LOBP.rem
Primary Remaining Lifetime Ortho Benefit
-
If LOBP.max has no value, then LOBP.rem = 9,999,999.99
-
If LOBP.max = 0, then LOBP.rem = 0
-
If LOBP.max > 0, then LOBP.rem = LOBP.max - LOBP.used
-
-
Set the Primary Remaining Benefit (BP.rem) equal to the Primary Remaining Lifetime Ortho Benefit (LOBP.rem).
BP.rem = LOBP.rem
-
-
For a non-orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
Calculate the Primary Remaining Annual Individual Benefit:
Terms
AIBP.max
Primary Maximum Annual Individual Benefit
AIBP.used
Primary Used Annual Individual Benefit
AIBP.rem
Primary Remaining Annual Individual Benefit
-
If AIBP.max has no value, then AIBP.rem = 9,999,999.99
-
If AIBP.max = 0, then AIBP.rem = 0
-
If AIBP.max > 0, then AIBP.rem = AIBP.max - AIBP.used
-
-
Calculate the Primary Remaining Annual Family Benefit:
Terms
AFBP.max
Primary Maximum Annual Family Benefit
AFBused
Primary Used Annual Family Benefit
AFBrem
Primary Remaining Annual Family Benefit
-
If AFBP.max has no value, then AFBP.rem = 9,999,999.99
-
If AFBP.max = 0, then AFBP.rem = 0
-
If AFBP.max > 0, then AFBP.rem = AFBP.max - AFBP.used
-
-
Calculate the Primary Remaining Benefit. Take the lesser of AIBP.rem and AFBP.rem, and then set BP.rem equal to that lesser amount.
BP.rem = min (AIBP.rem ; AFBP.rem)
-
-
-
Use the Primary Remaining Benefit to adjust the Max Primary Insurance Portion as needed.
Terms
IP.max
Max Primary Insurance Portion
BP.rem
Primary Remaining Benefit
Do one of the following:
-
If IP.max <= BP.rem, there is enough remaining benefit to cover the entire amount that is expected to be paid by the carrier. The Max Primary Insurance Portion does not change.
IP.max = IP.max
-
If IP.max > BP.rem, the remaining benefits covers none or only a portion of the amount that is expected to be paid by the carrier. Set the Max Primary Insurance Portion (IP.max) equal to the Primary Remaining Benefit (BP.rem).
IP.max = BP.rem
-
-
Calculate the Secondary Remaining Deductible.
Term
DS.rem
Secondary Remaining Deductible
Note: No value or a zero (0) for a required deductible both indicate that no deductible is required.
-
Do one of the following:
-
For an orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
Calculate the Secondary Remaining Annual Individual Ortho Deductible:
Terms
AIODS.req
Secondary Required Annual Individual Ortho Deductible
AIODS.met
Secondary Met Annual Individual Ortho Deductible
AIODS.rem
Secondary Remaining Annual Individual Ortho Deductible
-
If AIODS.req has no value, then AIODS.rem = 0
-
If AIODS.req = 0, then AIODS.rem = 0
-
If AIODS.req > 0, then AIODS.rem = AIODS.req - AIODS.met
-
-
Set the Secondary Remaining Deductible (DS.rem) equal to the Secondary Remaining Annual Individual Ortho Deductible (AIODS.rem).
DS.rem = AIODS.rem
-
-
For a non-orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
For the Lifetime Individual Deductible, calculate the Secondary Remaining Lifetime Individual Deductible:
Terms
LIDS.req
Secondary Required Lifetime Individual Deductible
LIDS.met
Secondary Met Lifetime Individual Deductible
LIDS.rem
Secondary Remaining Lifetime Individual Deductible
-
If LIDS.req has no value, then LIDS.rem = 0
-
If LIDS.req = 0, then LIDS.rem = 0
-
If LIDS.req > 0, then LIDS.rem = LIDS.req - LIDS.met
-
-
For the Annual Family Deductible, calculate the Secondary Remaining Annual Family Deductible:
Terms
AFDS.req
Secondary Required Annual Family Deductible
AFDS.met
Secondary Met Annual Family Deductible
AFDS.rem
Secondary Remaining Annual Family Deductible
-
If AFDS.req has no value, then AFDS.rem = 0
-
If AFDS.req = 0, then AFDS.rem = 0
-
If AFDS.req > 0, then AFDS.rem = AFDS.req - AFDS.met
-
-
For the Annual Individual Deductible, calculate the Secondary Remaining Annual Individual Deductible:
Terms
AIDS.req
Secondary Required Annual Individual Deductible
AIDS.met
Secondary Met Annual Individual Deductible
AIDS.rem
Secondary Remaining Annual Individual Deductible
-
If AIDS.req has no value, then AIDS.rem = 0
-
If AIDS.req = 0, then AIDS.rem = 0
-
If AIDS.req > 0, then AIDS.rem = AIDS.req - AIDS.met
-
-
Calculate the Secondary Remaining Deductible. Take the lesser of LIDS.rem, AFDS.rem, and AIDS.rem, and set DS.rem equal to that lesser amount.
DS.rem = min (LIDS.rem ; AFDS.rem ; AIDS.rem)
-
-
-
-
Calculate the Secondary Insurance Portion.
Terms
Isec
Secondary Insurance Portion
Aproc
Amount Charged (the procedure's Amount)
AS.max
Secondary Max Allowable Amount (from the secondary plan's Max allowable amount fee schedule)
AS.min
Secondary Min Allowable Amount
AS.pay
Secondary Payment Table Amount (from the Amount column in the plan's payment table)
CS.pat
Secondary Patient Copay (from the Copayment $ column in the secondary plan's coverage table)
CS.ins
Secondary Insurance Coverage Percentage (from the Coverage % column in the secondary plan's coverage table)
CS.exc
Secondary Patient Copay Exception or Secondary Insurance Coverage Exception (any applicable exceptions, as indicated in the EXC column, in the secondary plan's coverage table)
OS.ins
Secondary Insurance Estimate Override (from the procedure's Insurance Estimate Overrides; entered and locked automatically, or entered manually)
Do one of the following:
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is selected for the plan, do the following:
-
Calculate the Secondary Min Allowable. Because the calculations for the Secondary Insurance Portion require that AS.max not exceed Aproc, take the lesser of Aproc and AS.max, and then set AS.min equal to that lesser amount.
AS.min = min (Aproc ; AS.max)
-
Calculate the Secondary Insurance Portion. Do one of the following:
-
Without a Secondary Insurance Estimate Override:
-
For a coverage table based on patient copayments, do the following:
-
Determine the Secondary Patient Copay.
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, it is ignored currently. Use the default copay.
CS.pat = CS.pat
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default copay.
CS.pat = CS.pat
-
-
Calculate the Secondary Insurance Portion. Use one of the following methods for coordinating benefits:
-
Traditional: Subtract CS.pat from AS.min, and then set Isec equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Isec equal to zero.
Isec = max (0; AS.min - CS.pat)
-
Maintenance of Benefits: Subtract Wsec, Ipri, and CS.pat from Aproc, and then set Isec equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Isec equal to zero.
Isec = max (0 ; Aproc - Wsec - Ipri - CS.pat)
-
Carve Out/Non-duplication: Subtract CS.pat and Ipri from AS.min, and then set Isec equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Isec equal to zero.
Isec = max (0 ; AS.min - CS.pat - Ipri)
-
-
-
For a coverage table based on insurance coverage percentages, do one of the following:
-
If a procedure is listed in the payment table, take the greater of AS.min and AS.pay, and then set Isec equal to that greater amount.
Isec = max (AS.min ; AS.pay)
-
If a procedure is not listed in the payment table, do the following:
-
Determine the Secondary Insurance Coverage Percentage. Do one of the following:
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the following exception types to determine the coverage:
-
Not covered. The carrier does not have a portion, so set CS.ins equal to zero.
CS.ins = 0
-
Frequency. Do one of the following:
-
For a procedure with a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, do one of the following:
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for the same treatment area, set CS.ins equal to zero.
CS.ins = 0
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for a different treatment area, use the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.ins
-
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set CS.ins equal to zero
CS.ins = 0
-
-
For a procedure without a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, use the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.ins
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set CS.ins equal to zero.
CS.ins = 0
-
-
-
Downgrade. Use the exception instead of the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.exc
-
Age limitation. Do one of the following:
-
If the patient's age does not exceed the specified age, use the exception instead of the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.exc
-
If the patient's age exceeds the specified age, use the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.ins
-
-
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.ins
-
-
Calculate the Secondary Insurance Portion. Use one of the following methods for coordinating benefits:
-
Traditional: Multiply AS.min and CS.ins, and then set Isec equal to that product unless that product is less than zero, in which case, set Isec equal to zero.
Isec = max (0 ; AS.min x CS.ins)
-
Maintenance of Benefits: Subtract Ipri from AS.min, multiply that difference and CS.ins, and then set Isec equal to the resulting product unless that product is less than zero, in which case, set Isec equal to zero.
Isec = max (0 ; (AS.min - Ipri) x CS.ins)
-
Carve Out/Non-duplication: Multiply AS.min and CS.ins, subtract Ipri from that product, and then set Isec equal to the resulting difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Isec equal to zero.
Isec = max (0 ; (AS.min x CS.ins) - Ipri)
-
-
-
-
-
With a Secondary Insurance Estimate Override, use one of the following methods for coordinating benefits:
-
Traditional: Take the greater of OS.ins and AS.min, and then set Isec equal to that greater amount unless that greater amount is less than zero, in which case, set Isec equal to zero.
Isec = max (0; min (OS.ins ; AS.min))
-
Maintenance of Benefits: Set Isec equal to the override.
Isec = OS.ins
-
Carve Out/Non-duplication: Set Isec equal to the override.
Isec = OS.ins
-
-
-
-
If a Max allowable amount fee schedule is not selected for the plan, do one of the following:
-
Without a Secondary Insurance Estimate Override, do one of the following:
-
For a coverage table based on patient copayments, do the following:
-
Determine the Secondary Patient Copay.
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, it is ignored currently. Use the default copay.
CS.pat = CS.pat
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default copay.
CS.pat = CS.pat
-
-
Calculate the Secondary Insurance Portion. Use one of the following methods for coordinating benefits:
-
Traditional: Subtract CS.pat from Aproc, and then set Isec equal to that difference.
Isec = Aproc - CS.pat
-
Maintenance of Benefits: Subtract Ipri and CS.pat from Aproc, and then set Isec equal to that difference.
Isec = Aproc - Ipri - CS.pat
-
Carve Out/Non-duplication: Subtract CS.pat and Ipri from Aproc, and then set Isec equal to that difference.
Isec = Aproc- CS.pat - Ipri
-
-
-
For a coverage table based on insurance coverage percentages, do one of the following:
-
If a procedure is listed in the payment table, set Isec equal to AS.pay.
Isec = AS.pay
-
If a procedure is not listed in the payment table, do the following:
-
Determine the Secondary Insurance Coverage Percentage. Do one of the following:
-
If there is an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the following exception types to determine the coverage:
-
Not covered. The carrier does not have a portion, so set CS.ins equal to zero.
CS.ins = 0
-
Frequency. Do one of the following:
-
For a procedure with a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, do one of the following:
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for the same treatment area, set CS.ins equal to zero.
CS.ins = 0
-
If the same procedure was posted previously (within the coverage period and within the specified frequency limit) for a different treatment area, use the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.ins
-
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set CS.ins equal to zero
CS.ins = 0
-
-
For a procedure without a treatment area, do one of the following:
-
If the procedure's date does not exceed the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, use the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.ins
-
If the procedure's date exceeds the specified frequency limit since the coverage start date, set CS.ins equal to zero.
CS.ins = 0
-
-
-
Downgrade. Use the exception instead of the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.exc
-
Age limitation. Do one of the following:
-
If the patient's age does not exceed the specified age, use the exception instead of the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.exc
-
If the patient's age exceeds the specified age, use the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.ins
-
-
-
If there is not an exception for the procedure in the coverage table, use the default coverage.
CS.ins = CS.ins
-
-
Calculate the Secondary Insurance Portion. Use one of the following methods for coordinating benefits:
-
Traditional: Multiply Aproc and CS.ins, and then set Isec equal to that product.
Isec = Aproc x CS.ins
-
Maintenance of Benefits: Subtract Ipri from Aproc, multiply that difference and CS.ins, and then set Isec equal to the resulting product.
Isec = (Aproc - Ipri) x CS.ins
-
Carve Out/Non-duplication: Multiply Aproc and CS.ins, subtract Ipri from that product, and then set Isec equal to that product.
Isec = (Aproc x CS.ins) - Ipri
-
-
-
-
-
With a Secondary Insurance Estimate Override, set Isec equal to the override.
Isec = OS.ins
-
-
-
Use the Secondary Remaining Deductible to set the Max Secondary Insurance Portion.
Terms
IS.max
Max Secondary Insurance Portion
Isec
Secondary Insurance Portion
DS.rem
Secondary Remaining Deductible
Subtract DS.rem from Isec, and then set Imax equal to that difference.
Imax = Isec - Drem
-
Calculate the Secondary Remaining Benefit.
Terms
BS.rem
Secondary Remaining Benefit
Note: No value for a maximum indicates unlimited benefits; zero (0) indicates no benefits.
Do one of the following:
-
For an orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
Calculate the Secondary Remaining Lifetime Ortho Benefit:
Terms
LOBS.max
Secondary Maximum Lifetime Ortho Benefit
LOBS.used
Secondary Used Lifetime Ortho Benefit
LOBS.rem
Secondary Remaining Lifetime Ortho Benefit
-
If LOBS.max has no value, then LOBS.rem = 9,999,999.99
-
If LOBS.max = 0, then LOBS.rem = 0
-
If LOBS.max > 0, then LOBS.rem = LOBS.max - LOBS.used
-
-
Set the Secondary Remaining Benefit (BS.rem) equal to the Secondary Remaining Lifetime Ortho Benefit (LOBS.rem).
BS.rem = LOBS.rem
-
-
For a non-orthodontic procedure, do the following:
-
Calculate the Secondary Remaining Annual Individual Benefit:
Terms
AIBS.max
Secondary Maximum Annual Individual Benefit
AIBS.used
Secondary Used Annual Individual Benefit
AIBS.rem
Secondary Remaining Annual Individual Benefit
-
If AIBS.max has no value, then AIBS.rem = 9,999,999.99
-
If AIBS.max = 0, then AIBS.rem = 0
-
If AIBS.max > 0, then AIBS.rem = AIBS.max - AIBS.used
-
-
Calculate the Secondary Remaining Annual Family Benefit:
Terms
AFBS.max
Secondary Maximum Annual Family Benefit
AFBS.used
Secondary Used Annual Family Benefit
AFBS.rem
Secondary Remaining Annual Family Benefit
-
If AFBS.max has no value, then AFBS.rem = 9,999,999.99
-
If AFBS.max = 0, then AFBS.rem = 0
-
If AFBS.max > 0, then AFBS.rem = AFBS.max - AFBS.used
-
-
Calculate the Secondary Remaining Benefit. Take the lesser of AIBS.rem and AFBS.rem, and then set BS.rem equal to that lesser amount.
BS.rem = min (AIBS.rem ; AFBS.rem)
-
-
-
Use the Secondary Remaining Benefit to adjust the Max Secondary Insurance Portion as needed.
Terms
IS.max
Max Secondary Insurance Portion
BS.rem
Secondary Remaining Benefit
Do one of the following:
-
If IS.max<= BS.rem, there is enough remaining benefit to cover the entire amount that is expected to be paid by the carrier. The Max Secondary Insurance Portion does not change.
IS.max = IS.max
-
If IS.max > BS.rem, the remaining benefits covers none or only a portion of the amount that is expected to be paid by the carrier. Set the Max Secondary Insurance Portion (IS.max) equal to the Secondary Remaining Benefit (BS.rem).
IS.max = BS.rem
-
-
Calculate the final amounts for the Total Insurance Portion, the Max Write-off, and the Max Patient Portion.
Terms
Itot
Total Insurance Portion (for dual coverage)
IP.max
Max Primary Insurance Portion
IS.max
Max Secondary Insurance Portion
Aproc
Amount Charged (the procedure's Amount)
Pmax
Max Patient Portion (for dual coverage)
Wmax
Max Write-off (for dual coverage)
Do one of the following:
-
For either the Maintenance of Benefits or the Carve out/Non-duplication method of coordinating benefits, do the following:
-
Calculate the Total Insurance Portion. Add IP.max and IS.max, and then set Itot equal to that sum.
Itot = sum (IP.max + IS.max)
-
Do one of the following:
-
If Itot >= Aproc, do the following:
-
Set the Total Insurance Portion (Itot) equal to Aproc.
Itot = Aproc
-
Set the Max Patient Portion (Pmax) equal to zero.
Pmax = 0
-
Set the Max Write-off (Wmax) equal to zero.
Wmax = 0
-
-
If Itot < Aproc, do one of the following:
-
With the Insurance Sum (S) equal to Itot + Wmax, if S >= Aproc, do the following:
-
Set the Max Patient Portion (Pmax) equal to zero.
Pmax = 0
-
Do one of the following:
-
If S = Aproc, adjustments are not needed. The Max Write-off and the Total Insurance Portion stay the same.
Wmax = Wmax
Itot = Itot
-
If S > Aproc, make adjustments in the following order (until S = Aproc):
-
If S > Aproc, reduce Wmax until S = Aproc or until Wmax = 0, whichever comes first.
-
If Wmax = 0, and if S > Aproc, reduce Itot (by reducing IS.max) until S = Aproc.
-
-
-
-
With the Insurance Sum (S) equal to Itot + Wmax, if S < Aproc, do the following:
-
Calculate the Max Patient Portion. Subtract Itot and Wmax from Aproc, and then set Pmax equal to that difference.
Pmax = Aproc - Itot - Wmax
-
The Max Write-off and the Total Insurance Portion stay the same.
Wmax = Wmax
Itot = Itot
-
-
-
-
-
For the Traditional method of coordinating benefits, do the following:
-
Calculate the Total Insurance Portion. Add IP.max and IS.max, and then set Itot equal to that sum.
Itot = sum (IP.max + IS.max)
-
Calculate the Max Patient Portion. Subtract Wmax, IP.max, and IS.max from Aproc, and then set Pmax equal to that difference unless that difference is less than zero, in which case, set Pmax equal to zero.
Pmax= max (0; Aproc - Wmax - IP.max - IS.max)
-
Set the Sum of the Terms (s) equal to the sum of Wmax, IP.max, IS.max, and Pmax.
S = sum (Wmax + IP.max + IS.max + Pmax)
-
Do one of the following:
-
If S = Aproc, adjustments are not needed. The Max Write-off and the Total Insurance Portion stay the same.
Wmax = Wmax
Itot = Itot
-
If S > Aproc, make adjustments in the following order (until S = Aproc):
-
If S > Aproc, reduce Pmax until S = Aproc or until Pmax = 0, whichever comes first.
-
If Pmax = 0 and if S > Aproc, reduce Wmax until S = Aproc or until Wmax = 0, whichever comes first.
-
If Pmax = 0, if Wmax = 0, and if S > Aproc, reduce Itot (by reducing IS.max) until S = Aproc.
-
-
-
-